Introducing the Evans Income and Expense Statement Answer Key, a definitive resource that unravels the intricacies of financial analysis. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of income statements, expense classification, and their interplay in financial planning.
Delving into the nuances of financial management, we will explore the significance of income statements, identify various expense categories, and demonstrate their impact on overall financial health. Moreover, we will uncover strategies for expense control and effective budgeting, empowering individuals and organizations to make informed financial decisions.
Income Statement Analysis
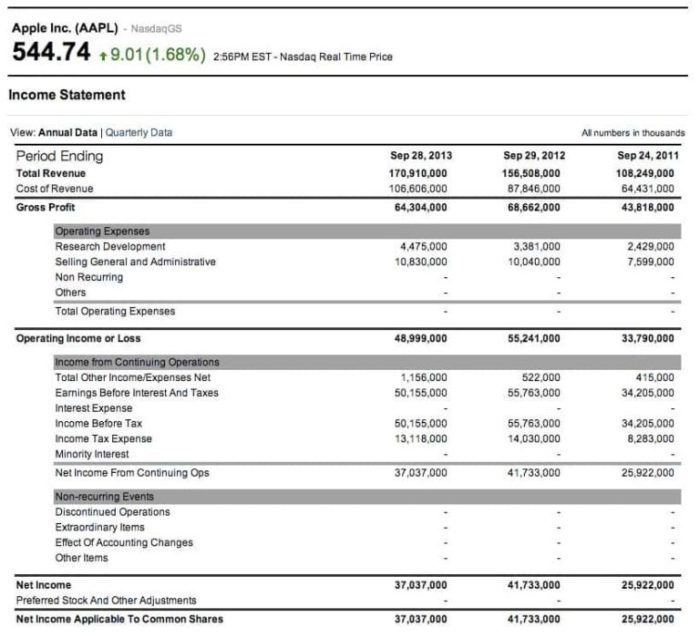
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, is a financial statement that summarizes a company’s financial performance over a specific period of time, typically a quarter or a year. It provides a detailed overview of the company’s revenues, expenses, and profits.
The income statement is an important financial document for several reasons. First, it provides investors and creditors with insights into a company’s profitability and financial health. Second, it can be used to track a company’s performance over time and identify trends.
Third, it can be used to make informed decisions about future investments and business operations.
Key Components of an Income Statement
- Revenue:Revenue is the total amount of money earned by a company from its core business activities. It is typically classified into different categories, such as sales revenue, service revenue, and interest revenue.
- Expenses:Expenses are the costs incurred by a company in generating revenue. They are typically classified into different categories, such as cost of goods sold, selling and administrative expenses, and research and development expenses.
- Profit:Profit is the difference between revenue and expenses. It can be further classified into gross profit, operating profit, and net profit.
Expense Analysis
Expenses are an important part of an income statement. They can be classified into different types based on their nature and how they are used in the business.
Types of Expenses
- Cost of goods sold (COGS):COGS is the cost of the products or services that a company sells. It includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
- Selling and administrative expenses (S&A):S&A expenses are the costs incurred in selling and marketing a company’s products or services. They include the cost of sales staff, advertising, and customer service.
- Research and development (R&D):R&D expenses are the costs incurred in developing new products or services. They include the cost of research, development, and testing.
- Depreciation and amortization:Depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses that represent the decline in value of assets over time. Depreciation is used for tangible assets, such as buildings and equipment, while amortization is used for intangible assets, such as patents and trademarks.
Income and Expense Comparison, Evans income and expense statement answer key
| Category | Income | Expenses |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | $100,000 | – |
| Cost of goods sold | – | $50,000 |
| Selling and administrative expenses | – | $20,000 |
| Research and development expenses | – | $10,000 |
| Depreciation and amortization | – | $5,000 |
| Profit | $15,000 | $85,000 |
The income and expense comparison table shows that the company has a net profit of $15,000. This means that the company’s revenue exceeds its expenses.
The table also shows that the company’s largest expense is cost of goods sold, which accounts for 50% of total expenses. This is followed by selling and administrative expenses, which account for 20% of total expenses.
Financial Planning
An income statement can be used for financial planning in several ways. First, it can be used to create a budget. A budget is a plan for how a company will spend its money over a specific period of time.
It can be used to ensure that the company has enough money to cover its expenses and achieve its financial goals.
Second, an income statement can be used to forecast future financial performance. A forecast is a prediction of how a company’s financial performance will change in the future. It can be used to make informed decisions about future investments and business operations.
General Inquiries: Evans Income And Expense Statement Answer Key
What is the purpose of an income statement?
An income statement provides a snapshot of a company’s financial performance over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It summarizes the company’s revenues, expenses, and profits, allowing stakeholders to assess its financial health and profitability.
How are expenses classified in an income statement?
Expenses are typically classified into three main categories: operating expenses, non-operating expenses, and income taxes. Operating expenses are directly related to the company’s core business activities, while non-operating expenses are indirect expenses that are not directly tied to operations.
What is the relationship between income and expenses?
Income and expenses are inversely related. Higher expenses can reduce income, while higher income can lead to increased expenses. Therefore, it is crucial for companies to strike a balance between maximizing income and controlling expenses to achieve optimal financial performance.